- Climate change is already affecting people’s lives in a variety of ways.
- Global warming is the biggest health threat facing humanity, the World Health Organization says.
- It’s also making people rethink family planning choices and putting properties at risk of becoming uninsurable.
- Disruptions to supply chains because of extreme weather are shaking the global economy.
How is climate change affecting you?
You may think the biggest impacts lie far away – in terms of time or geography. But global warming is already changing the way many of us live or think.
1. Health suffers because of climate change
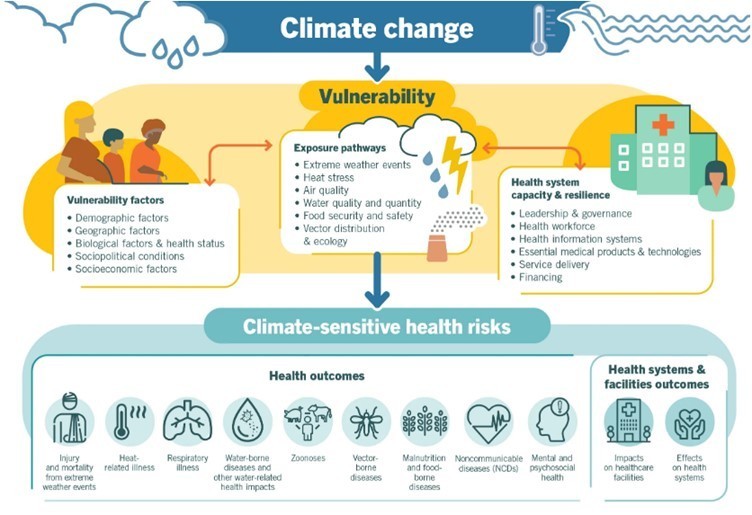
Climate change is the biggest health threat facing humanity, the World Health Organization says, estimating that it will cause around a quarter of a million additional deaths each year in 2030-50. These will mainly be from malnutrition, malaria, diarrhoea and heat stress.
However, climate change is already having more subtle effects on health and wellbeing. Spring is beginning earlier in many places, meaning there’s a higher pollen count. This is bad news for allergy sufferers. Higher temperatures in the United States made the pollen season 11-27 days longer between 1995 and 2011, the Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America says.
Rising temperatures also contribute to deepening air quality, which can increase the risk and severity of asthma attacks.
2. Climate change is raising the cost of living
COVID-19 has received most of the blame for recent global supply chain problems, but climate change is also having an impact. When supply chains are shaken, this impacts the availability and cost of goods.
Freezing weather in Texas in February 2021 triggered the United States’ most severe energy blackout of all time, leading to shutdowns at three major semiconductor plants and adding to the global shortage of microchips.
The cost of living is also soaring because of the global surge in energy prices. While Russia’s war on Ukraine is driving much of this now, climate change is also a factor.
“Companies face up to $120 billion in costs from environmental risks in their supply chains by 2026,” according to research published in 2021 by CDP, a nonprofit that runs the world’s largest environmental disclosure system. This will include increased costs for raw materials, and because of regulatory changes such as carbon pricing as the world addresses environmental crises, the report says.
3. Warming oceans are threatening our way of life
Sea level rises could pose the biggest threat to global supply chainspotentially putting ports and coastal infrastructure out of action. Higher sea temperatures may also cause more severe storms in tropical parts of the world, posing a threat to life and infrastructure.
The sea is home to most of our biodiversity, and 3 billion people globally rely on it for their livelihoods, according to the UN. However, carbon emissions from human activity are causing ocean warming, acidification and oxygen lossputting large numbers of marine-related jobs at risk, it says.
Climate change poses an urgent threat demanding decisive action. Communities around the world are already experiencing increased climate impacts, from droughts to floods to rising seas. The World Economic Forum’s Global Risks Report continues to rank these environmental threats at the top of the list.
To limit global temperature rise to well below 2°C and as close as possible to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels, it is essential that businesses, policy-makers, and civil society advance comprehensive near- and long-term climate actions in line with the goals of the Paris Agreement on climate change.
The World Economic Forum’s Climate Initiative supports the scaling and acceleration of global climate action through public and private-sector collaboration. The Initiative works across several workstreams to develop and implement inclusive and ambitious solutions.
This includes the Alliance of CEO Climate Leaders, a global network of business leaders from various industries developing cost-effective solutions to transitioning to a low-carbon, climate-resilient economy. CEOs use their position and influence with policy-makers and corporate partners to accelerate the transition and realize the economic benefits of delivering a safer climate.
Contact us to get involved.
4. People might have fewer babies
People are reason citing the climate crisis as a major why they may decide to have fewer or even no children. According to a study in the United States, a third of women said they will reduce their anticipated family size because of it.
However a similar number of the more than 2,800 American women surveyed by Modernfertility.com said the issue has made them decide to have children sooner. The study says this is because it’s either made them focus more on what’s important to them or given them a sense of urgency.
5. Your property could become uninsurable
Insurance is something that nearly everyone has, but climate change poses a “systemic risk” to the sector, according to professional services company Grant Thornton.
Extreme weather events led to insured losses of $105 billion in 2021the fourth-highest level since 1970, according to preliminary estimates by Swiss Re, one of the world’s leading providers of reinsurance and insurance.
This not only potentially makes insurance more expensive for everyone, but it also means some assets could become uninsurable. One in 25 Australian homes could be uninsurable by 2030according to the Climate Council.
6. Increased chance of another pandemic
Climate change makes new pandemics more likely, because as temperatures increase, wild animals will be forced to change habitats. This could lead to them living nearer to human populations, Increasing the chances of a virus jumping between species and causing the next pandemic, according to a report published by the scientific journal Nature.
“Geographic range shifts” will mean mammals encounter each other for the first time, and in doing so will share thousands of viruses, the report says. Even keeping global warming under 2°C this century “will not reduce future viral sharing”, the scientists note.
The first human trial of a COVID-19 vaccine was administered this week.
CEPI, launched at the World Economic Forum, provided funding support for the Phase 1 study. The organization this week announced their seventh COVID-19 vaccine project in the fight against the pandemic.
The Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI) was launched in 2017 at the Forum’s Annual Meeting – bringing together experts from government, business, health, academia and civil society to accelerate the development of vaccines against emerging infectious diseases and to enable access to these vaccines during outbreaks.
Coalitions like CEPI are made possible through public-private partnerships. The World Economic Forum is the trusted global platform for stakeholder engagement, bringing together a range of multistakeholders from business, government and civil society to improve the state of the world.
Organizations can partner with the Forum to contribute to global health solutions. Contact us to find out how.
The World Economic Forum is committed to helping limit global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels to stave off catastrophe. It aims to work with leaders to increase climate commitments, collaborate with partners to develop private initiatives, and provide a platform for innovators to realize their ambition and contribute solutions.
.